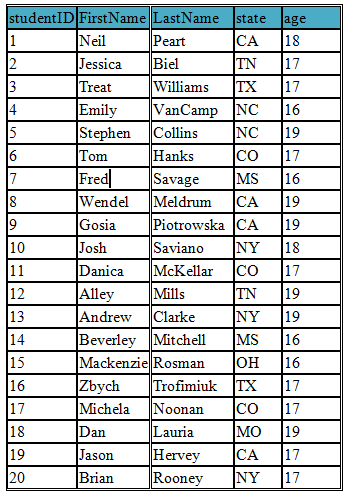
In this lesson we are working with the student table which includes the following fields
(studentID, FirstName, LastName, state, age)
SQL SELECT Statement
The select statement is used to fetch data from a database
Using following query we select only three fields (FirstName, LastName, age) from our student table
SELECT FirstName, LastName,age FROM student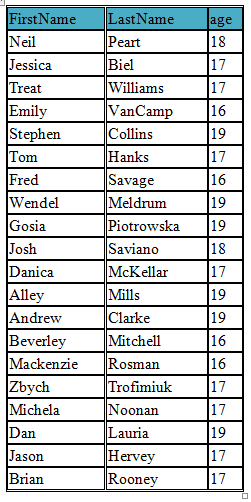
WHERE Clause
Using WHERE clause we can get specified records based on a given condition or number of conditions
We also use WHERE clause when we need to join tables in a database
SELECT * FROM student WHERE state="NY"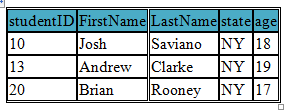
SQL AND Operator
The AND operator displays records only if both or number of conditions are true
We can combine number of conditions using AND operator
SELECT * FROM student WHERE state='NY' AND age='17'
SQL OR Operator
The OR operator displays records if either the first condition OR the second condition is true.
SELECT * FROM student WHERE state='NY' OR age='17'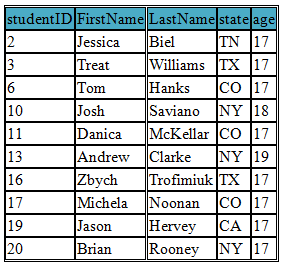
LIMIT Statement
limit statement is used to select limited number of records
SELECT studentID, FirstName, LastName, state FROM student LIMIT 5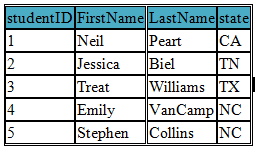
SELECT * FROM student LIMIT 10, 7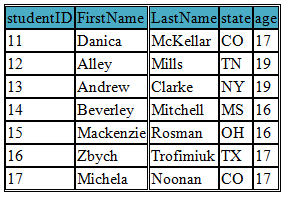
SELECT DISTINCT Statement
In a database table a column may contain duplicated records and SELECT DISTINCT Statement is used to select only distinct values from the table
SELECT DISTINCT age FROM student 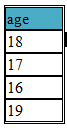
SQL IN Operator
Using SQL IN Operator we can specify multiple values in a WHERE Clause rather than using several OR statements
In this example we are selecting students in the age of 16 and 17
SELECT studentID, FirstName, LastName, age FROM student
WHERE age IN('17','19') ORDER BY age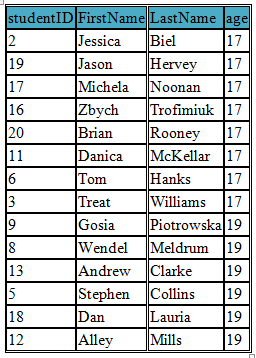
SQL NOT IN Operator
NOT IN Operator is the opposite of SQL IN operator
In this example we have selected students who are not in the age of 17 and 19
SELECT studentID, FirstName, LastName, age FROM student
WHERE age NOT IN('17','19') ORDER BY age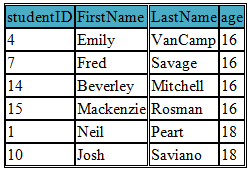
ORDER BY
ORDER BY Keyword allows us to sort the records in Ascending or Descending order and ORDER BY Keyword sorts the records in ascending by default
ORDER BY ASC
ORDER BY ASC sorts the records in ascending order
In the following example we select all the students in the student table and sort them in ascending order of age
SELECT studentID, FirstName, LastName, age FROM student
ORDER BY age ASC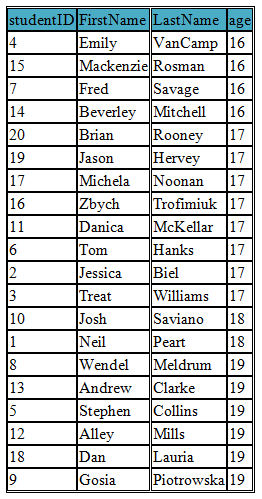
ORDER BY DESC
The following example selects all the students in the student table and sorts them in descending order of age
SELECT studentID, FirstName, LastName, age FROM student
ORDER BY age DESC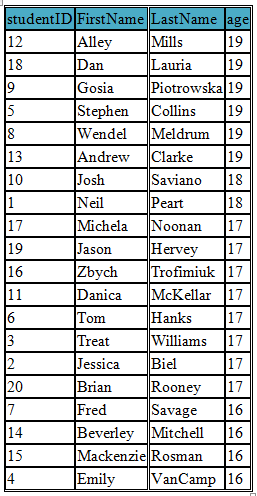

Just a note that in IBM Db2 SQL the LIMIT functionality is implemented using FETCH FIRST n ROWS ONLY